Add Unallocated Space to C Drive in Windows Server 2019/2022/2025 — Different Cases & How to Do It Without Losing Data
Short summary: Running out of space on the C: (system) drive is common on Windows Server 2022. This article explains multiple safe approaches to add unallocated space to C drive in Windows Server 2019 2022 2025 without data loss — using built-in tools (Disk Management and DiskPart), VM/Hypervisor storage operations, and a server-grade third-party tool, IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server. We also cover caveats, a quick how-to per scenario, and frequently asked questions.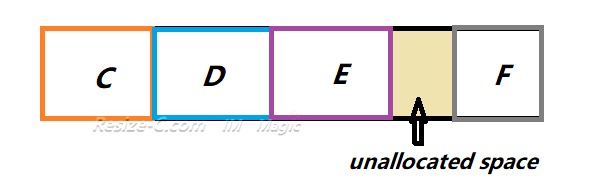
Quick Links
- How to add unallocated space to C drive usng IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server
- Unallocated space already immediately after C
- Unallocated space exists on the same disk but not contiguous
- Unallocated space is on a different physical disk
Why the problem happens (quick technical background)
Windows can extend a basic volume only when the unallocated space is on the same disk and immediately follows the volume you want to extend. If there is another partition (for example a Recovery or D: partition) between C: and the unallocated area, Disk Management will not let you extend C:, and the Extend Volume option will be greyed out. These rules are documented in Microsoft’s Disk Management guidance.
Add/Merge Unallocated Space to Server 2019/2022/2025 C Drive Using Resizer Server
IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server (often referenced as Partition Resizer Server) is a server edition of IM-Magic’s partition tool designed for Windows Server platforms. It supports Windows Server editions including Server 2022 2025 etc. and offers functions to shrink, move, and extend the system partition without destroying data — which is exactly what you need when the unallocated space is non-contiguous or when you need to move partitions.
What it does (key capabilities)
- Move partitions so unallocated space becomes contiguous with C:.
- Shrink any volumes to create unallocated space that can be added to C:.
- Extend system (boot) partition safely without deleting data.
- Provide a Server edition for production Windows Server OSes.
How to Use IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server in a Typical Non-Destructive Workflow
Video: How to create and move unallocated space to C drive
Back up your system first. (IM-Magic Partition Resizer includes a "Copy Disk" feature that provides 1:1 data cloning along with all disk properties for complete disk backup. See: How to backup disk)
- Download and install the Server Edition.
- Open the tool, select the partition to shrink (for example, D:), and shrink it to create unallocated space. (If unallocated space already exists, proceed to the next step.)
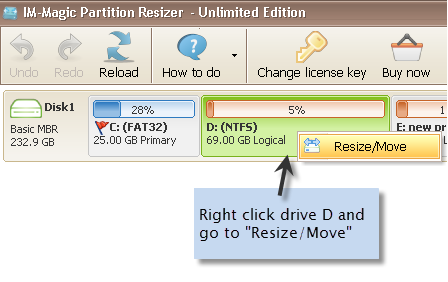
- If the unallocated space is not contiguous, right click the partition that stands next to the unallocated space, choose option Resize/Move", and then move the whole partition right or left to change the unallocated space location. Note: Use the tool’s Move/Resize feature to slide partitions so the location of the unallocated space is adjusted. Move each partition that blocks it until the unallocated block is immediately after C:.
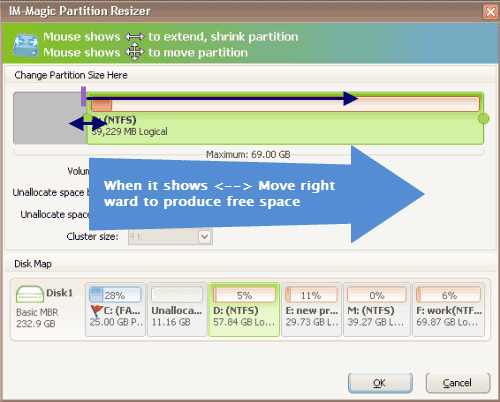
Shrink other large partition to produce free space for C drive
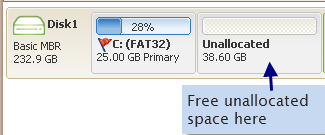
- When the unallocated space is adjacent to the C: drive, right-click the C: drive in Partition Resizer Server, choose the option “Resize/Move Partition,” and extend C: by dragging the partition boundary to claim the unallocated space. Click OK.
- Click “Apply Changes” and follow the tool’s prompts.
Important Caution: Make sure to click OK in every dialog box after making changes. All changes are virtual and will only be applied to your system once you click Apply Changes at the end.
Also read: How to move unallocated space, extend server 2022 c drive
Different cases and the recommended method for each
Case A — Unallocated space already immediately after C: on the same physical disk
Best method: use built-in Disk Management or DiskPart. This is the simplest and safest path because Windows will perform the operation without moving any other partitions.
- Open Server Manager → Tools → Computer Management → Disk Management.
- Right-click the C: volume and choose Extend Volume….
- Follow the wizard to add the unallocated space to C: and apply.
DiskPart is the command line alternative (use diskpart, select the disk, select the volume and run extend) and can be scripted for automation. Remember to back up before making changes.
Note: This only works when the unallocated space is contiguous (immediately after) the C: volume. If it isn’t, Windows won’t let you extend using built-ins.
Case B — Unallocated space exists on the same disk but not contiguous (there is an intervening partition)
Options:
- Delete the intervening partition (only when that partition is expendable or can be recreated later). After deletion, the space becomes contiguous and Disk Management can extend C:. This risks data loss for that partition — back up first.
- Move the intervening partition so the unallocated space becomes adjacent to C:. Windows Disk Management can’t move partitions; you’ll need third-party partition software.
- Use a trusted third-party server partition tool that can move/shrink/extend system partitions without data loss (see IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server guide).
Note: Some partitions like EFI cannot be deleted by Windows built-in tools, however IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server can help move the EFI partition without losing data.
Case C — Unallocated space is on a different physical disk (or you want to expand across disks)
Windows basic volumes cannot extend across physical disks. Your choices:
- Use virtualization/hypervisor features to increase the virtual disk size and then rescan/extend inside the guest OS.
- Convert to a dynamic volume (not recommended in many server scenarios) to span disks, or use Storage Spaces.
- Move files from C: to another disk or add a new disk and change where large folders point (junctions or Folder Redirection).
If the server is a VM, the safest approach is to expand the virtual disk (vDisk) in the hypervisor, then scan disks in Windows and extend the partition. Always snapshot or back up before VM disk changes.
Option: upgrade your disk to another larger SSD or HDD. IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server can help migrate the OS disk to a larger disk without losing data.
Case D — You need zero downtime or cannot reboot (mission critical)
For production servers where downtime is limited, consider:
- Adding storage at the virtualization layer (expand vDisk) — usually no reboot required.
- Attaching a new disk and moving specific large data directories off C: (swap locations for pagefile, logs, or databases).
- Using partition software that supports online resizing for server OS.
Note: When extending an NTFS partition, if none of the following conditions occur, adding unallocated space to the C: drive on Windows Server 2022 using IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server will not require a reboot.
- #1. The beginning part of the C: drive has not been changed.
- #2. No EFI partition is involved in the process.
- #3. The C: drive is not formatted as FAT32.
If any of the above conditions apply, a reboot will be required when extending the C: drive, even when using IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server.
Practical checklist before you start
- Full backup of system and critical data (image backup recommended).
- Verify disk health (SMART check) — resizing on failing disks can cause irrecoverable loss.
- Confirm whether the server is physical or virtual — for VMs, expand the virtual disk first at the hypervisor layer.
- Ensure you have a bootable recovery media in case the system becomes unbootable.
- Schedule maintenance if changes may require a reboot.
Short troubleshooting & tips
Extend Volume still greyed out
This is almost certainly because the unallocated space is not immediately to the right of C: or exists on a separate disk. Use partition-moving software or remove intervening partitions after backing up.
After resizing, Windows won’t boot
If the boot configuration was altered, use Windows Server recovery (boot from installation media → Repair → Command Prompt) and run bootrec /fixmbr bootrec /fixboot and bootrec /rebuildbcd. Having a recent image backup simplifies recovery.
FAQ
Q: Will using IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server void vendor support?
A: Using third-party tools is generally allowed but may complicate vendor support paths. If the server is under strict vendor SLA, consult the vendor before making partition changes on supported machines. You can always email your case to support@resize-c.com for quick, free assistance.
Q: Do I need to convert MBR to GPT or vice versa?
A: You only need to convert if your operations require a specific partitioning style (for example resizing a disk larger than 2TB under MBR). Conversions can be risky — back up before conversion.
Q: Is there a free option?
A: IM-Magic offers free versions for PCs and demo/server editions; however, depending on the exact operation you may need the Server edition or bootable media.
Conclusion
Adding unallocated space to the C: drive in Windows Server 2022 can be straightforward when the unallocated space is contiguous and on the same disk (use Disk Management or DiskPart). For non-contiguous or more complex scenarios, IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server provides a reliable way to move and resize partitions without data loss — provided you follow best practices: back up, verify disk health, and test where possible. Always treat partition changes as high-risk maintenance and prepare recovery options beforehand.
Keywords: add unallocated space to C drive in Windows Server 2022, extend C drive Server 2022, IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server, extend volume without losing data.
More Related Articles You May Like
- Add unallocated space to c drive server 2022
- Move unallocated space nex to the C drive server 2022
- Unallocated space is not adjacent to the c drive
- Change the location of the unallocated space
- Merge unallocated space to c drive
- Cant merge unallocated space to c drive
- Merge unallocated space to c drive using CMD
- how to merge unallocated space to c drive extend volume greyed out
- How to combine nonadjacent unallocated space to the C drive
Related Product
- IM-Magic Partition Resizer Server - Partition space redistributing software that works for Windows Server 2003-2025.