How to Combine Nonadjacent Unallocated Space to the C Drive (Windows 11 & 10 or Server)
If you're searching for how to add nonadjacent unallocated space to the C drive, this guide explains the limits of built-in tools, when you may need to delete a partition, cases where you cannot delete system partitions (EFI/recovery), and why a third-party utility such as IM-Magic Partition Resizer can make the job easier and safer.
Why Windows Disk Management can’t always add nonadjacent unallocated space
Windows Disk Management can only extend the C: drive when the unallocated space is directly to the right (adjacent) of the C: partition. If the unallocated space is nonadjacent (a partition sits in between), the Extend Volume option will be unavailable.
Image1: Case#1 when partition C has adjacent unallocaed space
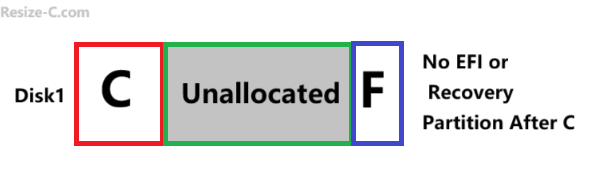 (Disk Management or Diskpart can only work under this condition)
(Disk Management or Diskpart can only work under this condition)
Image2: Case#2 when partition C has nonadjacent unallocaed space 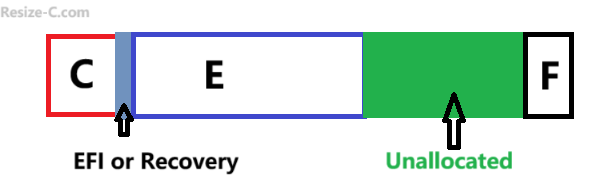 (Partition Resizer can move the unallocated space contiguous next to the C drive by moving the partitions that sit in between)
(Partition Resizer can move the unallocated space contiguous next to the C drive by moving the partitions that sit in between)
Use IM-Magic Partition Resizer — an easier&free solution
Free tool IM-Magic Partition Resizer can move partitions and merge nonadjacent unallocated space into your C: drive without forcing you to delete EFI or recovery partitions. These tools typically provide a wizard interface, support moving partitions on GPT/MBR, and let you preview changes before applying them. Still: back up before any operation. (IM-Magic Partition Resizer can backup data with its copy disk or copy partition feature.)
Video: How to create and move unallocated space to C drive
For Windows 11/10/8/7 => Download Partition Resizer Free [100% Free]
For Windows Server 2025-2003 => Download Partition Resizer Server [Free Demo]
Step-by-step with a partition tool (generalized)
- Install and run the partition tool (example: IM-Magic Partition Resizer).
- Select the partition(s) between C: and the unallocated space and choose "Move/Resize".
- Slide the whole partition right side one by one and click OK in each window, so that the unallocated space becomes adjacent to C:.
- Apply changes and wait for the tool to complete (will require a reboot if EFI sits there).
- Extend C: now that space is adjacent.
IM-Magic Partition Resizer offers 100% data and OS security when resizing and moving the partitions. Or you may also backup your system/data with Partition Resizer's copy partition or copy disk feature before the above changes if needed. Also read: How to backup disk or partition
General workflow: Adding nonadjacent unallocated space to C with Disk Management:
- Backup first. Always back up important files or create a system image before modifying partitions.
- Check layout. Open Disk Management (diskmgmt.msc) to view partition order and identify the nonadjacent unallocated space.
- If the partition between C: and the unallocated space is non-system:
- Delete that partition (after backup) to make unallocated space adjacent to C:.
- Right-click C: → Extend Volume → follow the wizard to add the unallocated space.
- If you cannot delete the partition (EFI, Recovery, or system):
- Do not delete EFI or recovery partitions; doing so can prevent booting or break recovery features.
- Use a partition tool that can move partitions and merge space without deleting EFI/recovery partitions.
When a partition sits in between — delete or move?
If the intervening partition contains data you can delete and you have backups, deleting it is the simplest path to make the unallocated space adjacent. However, if the partition is critical (EFI, Recovery) or you don’t want to lose its data, you should move the intervening partition using a partition manager that supports partition moving — this preserves data and results in adjacent unallocated space for C:.
Cases when you cannot delete a partition (EFI or Recovery)
- EFI System Partition (ESP): Contains boot files. Deleting breaks system boot.
- Microsoft Reserved Partition (MSR): Small reserved area used on GPT disks — should not be deleted.
- Windows Recovery Partition: Used for system recovery and troubleshooting — deleting removes recovery options.
For these partitions, do not attempt deletion; use a tool that can relocate or merge space without destroying these partitions.
FAQ
Q: Can I extend C: without deleting any partition?
A: Yes — if you use a tool that can move partitions so the unallocated space becomes adjacent to C:. Disk Management alone cannot do this.
Q: Is it safe to use third-party partition software?
A: Many tools are reliable, but any partition change carries risk. Always back up, read instructions, and choose reputable software.
Q: Will moving partitions erase my data?
A: Proper partition-moving operations preserve data, but failures (power loss, hardware issues) can cause data loss — which is why backups are essential.
Q: What if my disk uses MBR vs GPT?
A: Both partition styles can be handled by decent tools, but GPT has EFI partitions (do not delete). Confirm your disk type before making changes.
Summary: To combine nonadjacent unallocated space to the C drive on Windows 10 or 11 you can delete an intervening non-system partition (after backup) or, safer and easier, use a partition manager like IM-Magic Partition Resizer to move/merge space without deleting EFI or recovery partitions.
More Related Articles You May Like
- Add unallocated space to c drive server 2022
- Move unallocated space nex to the C drive server 2022
- Unallocated space is not adjacent to the c drive
- Change the location of the unallocated space
- Merge unallocated space to c drive
- Cant merge unallocated space to c drive
- Merge unallocated space to c drive using CMD
- how to merge unallocated space to c drive extend volume greyed out
- How to combine nonadjacent unallocated space to the C drive